MIDTERM REVIEW SHEET
LISTS: Most basic & versatile. Sequential container; programmer controls the order items appear.
SET: Like a list, but only unique items can exist. The computer controls the order of items. Can be ordered or unordered.
QUEUE: First in first out. Items enter the back and are popped off the front. Use .push(o) to add o to end. Use pop() to remove the object that is at the front of the queue. Faster than list/vector. Things like print jobs.
MAPS: Similar to dictionary in Python. Unique object : other object.
STACKS: Last in first out. Good for things that need to be reversed. isEmpty, push(o), pop(), and top() are all methods.
PRIORITY QUEUE: Like queues, but you can insert things in a specific order. top() instead of front() for highest priority item.
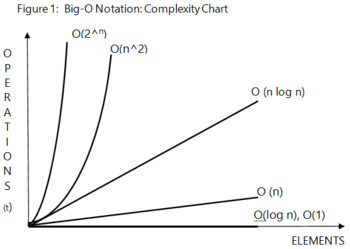
BINARY SEARCH Big(o): worst/average = O(log n); best = O(1)
| Algorithm | Best Case | Worst Case |
|---|---|---|
| Bubble Sort | ||
| Selection Sort | ||
| Insertion Sort | ||
| Merge Sort | ||
| Quick Sort | ||
 |
||
| BUBBLE SORT | ||
| do: | ||
| for each pair of adjacent elements: |
if the values are out of order:
swap the values
while the array is not sorted
- Look at each adjacent pair in the array
- Swap adjacent pairs if they are out of order
- Repeat until no swaps are made
worst-case runtime of bubble sort
INSERTION SORT
FOR EACH i FROM 1 TO size - 1
SET j TO i
SET item TO list[j]
WHILE j > 0 AND list[j - 1] > item
SET list[j] TO list[j - 1]
DECREMENT j BY 1
END WHILE
SET list[j] TO item
END FOR
The worst-case runtime is
compile with g++ --std=c++17 -Wall -o <output> <inputfile>.cpp
MERGE SORT
if the size of the List is at least 2
split the List into the left half and the right half
recursively sort left
recursively sort right
merge left and right into one List
end if
mergeSort ( list ) {
if ( list.size > 1 ) {
split( list, left, right );
mergeSort( left );
mergeSort( right );
merge( left, right, list );
}
}
split ( list, left, right ) {
for each item in the left half of list (less than or equal to middle index)
add the item to left
for each item in the right half of list (greater than middle index)
add the item to right
}
merge( left, right, list ) {
while both left and right have more items
if the left item is less than the right item
add the left item to list
else
add the right item to list
while left has more items
add the left item to list
while right has more items
add the right item to list
}
QUICK SORT
Begin with an array arr.
- Pick a pivot index.
Often at the end of the array.or find using a median of three algorithm - Declare two indices
jandi; and a temporary variabletempjis at the start of the arrayiis one less than the beginning of the array
- Do while
j < pivot:- If
arr[j] < arr[pivot]:i++- swap
arr[i]andarr[j]using temp variable- assign
temp = arr[i] - assign
arr[i] = arr[j] - assign
arr[j] = temp
- assign
j++
- If
- Now
j = i. Soi++. - Swap
arr[i]andarr[j]. Setpivot = i.- Now the
arr[pivot]is in the right spot. i.e. all items left of pivot are less than the pivot and all items greater than the pivot are greater than the pivot.
- Now the
- Finally, recursively return
quicksort(arr[:pivot - 1]) + [arr[pivot]] + quicksort(arr[pivot + 1:])
SELECTION SORT
- Find the smallest value in the unsorted portion
- Swap the value to the index after the end of the sorted portion
- Repeat until the unsorted portion is empty
Worst case:
- Each pass of the array is
- Up to
passes required to sort the list